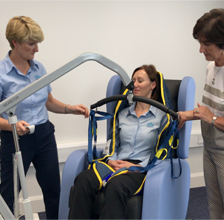
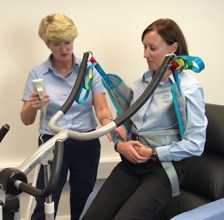
Manual handling is an area I am often asked about and it is important to know different techniques that will assist in safe patient transfers.
Today, I wanted to share with you PART 3, the third and final sequence in our 3 part manual handling series. You may have already had a chance to see PART 1 & PART 2 of our manual handling videos, providing tips and advice for hoisting in and out of the Sorrento and Monaco chairs. If not, you can view them here:
In the following video, manual handling adviser Mary Hickey from Elite Healthcare and myself answer your frequently asked questions.
The video contains useful tips including:
- How to choose the correct sling.
- Hoisting clients who have pressure injuries.
- How to identify the safe working load.
- Is it best to avoid frontal transfers?
We have answered numerous questions, but should you have any other queries you would like answered please get in touch and we will be happy to give our advice.
At Seating Matters, I have personally trained our Seating Specialists who are equipped to advise you and to answer any questions you may have. However, it is important to adhere to your own facility's guidelines and regulations. If you are unsure, it is best to ask the clinician in charge of manual handling in your facility or care trust.
Our Seating Specialists are trained to carry out thorough Seating Assessments. If you have a client in mind who would benefit from this complimentary service, please get it touch today.
* Note: The purpose of this blog is to give an overview of the product with some tips to consider on its use. This is not intended to be a substitute for professional or medical advice, diagnosis, prescription or treatment and does not constitute medical or other professional advice. For advice with your personal health or that of someone in your care, consult your doctor or appropriate medical professional.* Note: The Seating Assessment carried out by the Seating Specialist is to provide information and advice on the product only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional or medical advice, diagnosis, prescription or treatment, and does not constitute medical or other professional advice. For diagnosis or treatment of any medical problem, consult your own doctor or physician.